Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
成川 隆文; 濱口 修輔*; 高田 孝*; 宇田川 豊
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 411, p.112443_1 - 112443_12, 2023/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)For realizing a highly reliable fracture limit evaluation of fuel cladding tubes during loss-of-coolant accidents (LOCAs) in light-water reactors, we developed a method to quantify the fracture limit uncertainty of high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes. This method employs a hierarchical Bayesian model that can quantify uncertainty even with limited experimental data. The fracture limit uncertainty was quantified as a probability using the amount of oxidation (Equivalent cladding reacted: ECR) and the initial hydrogen concentration (the hydrogen concentration in the fuel cladding tubes before the LOCA-simulated tests) as explanatory variables. We divided the regression coefficients of this model into a hierarchical structure with an overall average term common to all types of fuel cladding tubes and a term representing differences among various types of fuel cladding tubes. This hierarchical structure enabled us to quantify the fracture limit uncertainty through the effective use of prior knowledge and data, even for high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes with a small number of data points. The fracture limits representing a 5% fracture probability with 95% confidence of the high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes evaluated by the hierarchical Bayesian model were higher than 15% ECR for the initial hydrogen concentrations of up to 700-900 wtppm and restraint loads below 535 N. These fracture limits were comparable to the limit of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tube, indicating that the burnup extension and use of the advanced fuel cladding tubes do not significantly lower the fracture limit of fuel cladding tubes. Further, we proposed a method to reduce the fracture limit uncertainty by using non-binary data, instead of the binary data, depending on the condition of the fuel cladding tube specimens after performing the LOCA-simulated test, thereby increasing the amount of information in the data.
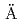 sp
sp HRL
HRL澤田 淳; 坂本 和彦*; 綿引 孝宜*; 今井 久*
SKB P-17-06, 154 Pages, 2023/08
An aim of Task 8, which was 8th modeling task of the SKB Task Forces on Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes, was to improve the knowledge of the bedrock-bentonite interface with regard to groundwater flow, mainly based on a set of data obtained by Bentonite Rock Interaction Experiment (BRIE) at 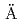 sp
sp . JAEA had developed an approach to Task 8 assuming that the discrete features dominate the delivery of groundwater to the bentonite columns emplaced into the vertically drilled boreholes from TASO tunnel floor, resulting in heterogeneous bentonite wetting behavior. This assumption was implemented as a FracMan Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) model for groundwater flow. Due to the assumption, no permeable rock matrix was implemented. The variability and uncertainty of this stochastic "HydroDFN" model was constrained by conditioning the model to match measured fracture location and orientation, and specific capacity (transmissivity) data observed at five probe boreholes. Groundwater from the HydroDFN being delivered to the bentonite columns, was modeled using Thames code with implementing a specific feature at the interface between the fractured rock mass and the bentonite. This modeling approach and the assumption of fracture dominated bentonite wetting appears to be able to provide a reasonable approximation to the observed heterogeneous bentonite wetting behavior of BRIE. We would suggest that a systematic investigation at pilot holes, including both geological mapping of the fractures and also testing of the hydraulic properties, might be required to get more practical prediction of heterogeneous wetting behavior in bentonite, as observed in BRIE.
. JAEA had developed an approach to Task 8 assuming that the discrete features dominate the delivery of groundwater to the bentonite columns emplaced into the vertically drilled boreholes from TASO tunnel floor, resulting in heterogeneous bentonite wetting behavior. This assumption was implemented as a FracMan Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) model for groundwater flow. Due to the assumption, no permeable rock matrix was implemented. The variability and uncertainty of this stochastic "HydroDFN" model was constrained by conditioning the model to match measured fracture location and orientation, and specific capacity (transmissivity) data observed at five probe boreholes. Groundwater from the HydroDFN being delivered to the bentonite columns, was modeled using Thames code with implementing a specific feature at the interface between the fractured rock mass and the bentonite. This modeling approach and the assumption of fracture dominated bentonite wetting appears to be able to provide a reasonable approximation to the observed heterogeneous bentonite wetting behavior of BRIE. We would suggest that a systematic investigation at pilot holes, including both geological mapping of the fractures and also testing of the hydraulic properties, might be required to get more practical prediction of heterogeneous wetting behavior in bentonite, as observed in BRIE.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez-Espinoza, V.*; Groudev, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; Bocanegra, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Berda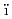 , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2022) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/05
The current HORIZON-2020 project on "Management and Uncertainties of Severe Accidents (MUSA)" aims at applying Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) in the modeling of Severe Accidents (SA), particularly in predicting the radiological source term of mitigated and unmitigated accident scenarios. Within its application part, the project is devoted to the uncertainty quantification of different severe accident codes when predicting the radiological source term of selected severe accident sequences of different nuclear power plant designs, e.g. PWR, VVER, and BWR. Key steps for this investigation are, (a) the selection of severe accident sequences for each reactor design, (b) the development of a reference input model for the specific design and SA-code, (c) the selection of a list of uncertain model parameters to be investigated, (d) the choice of an UQ-tool e.g. DAKOTA, SUSA, URANIE, etc., (e) the definition of the figures of merit for the UA-analysis, (f) the performance of the simulations with the SA-codes, and, (g) the statistical evaluation of the results using the capabilities, i.e. methods and tools offered by the UQ-tools. This paper describes the project status of the UQ of different SA codes for the selected SA sequences, and the technical challenges and lessons learnt from the preparatory and exploratory investigations performed.
崔 炳賢; 西田 明美; Li, Y.; 村松 健*; 高田 毅士*
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
2011年福島原子力発電所事故の後、原子力施設では設計を超える地震動への対策が求められている。確率論的地震リスク評価(SPRA)における不確実さは、低減できない偶然的不確実さと知識や情報収集によって低減可能な認識論的不確実さに分類される。SPRAの信頼度向上のために、知識不足による認識論的不確実さを低減することが必要である。本研究では、認識論的不確実さに関連し、モデル化手法による地震応答の違いに着目する。従来の質点系モデルと3次元有限要素モデルの2種類のモデルを用いて、偶然的不確実さを考慮した多様な入力地震動を用いた地震応答解析を実施する。各モデルで得られた原子炉建屋の床応答の違いについて定量的評価を行う。最後に、SPRAのフラジリティ評価において不確実さ評価結果をどのように活用するかについて議論する。
Zheng, X.; 伊藤 裕人; 玉置 等史; 丸山 結
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.333 - 344, 2016/03
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:67.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Large-scale computer programs simulate severe accident phenomena and often have a moderate-to-large number of models and input variables. Analytical solutions to uncertainty distributions of interested source terms are impractical, and influential inputs on outputs are hard to discover. Additionally, runs of such computer programs, or integral codes, are time-consuming and hence expensive. This article presents an integrated approach to the uncertainty and sensitivity analysis for nuclear reactor severe accident source terms, with an example which simulates an accident sequence similar to that occurred at Unit 2 of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant using an integral code, MELCOR. Monte Carlo based uncertainty analysis has been elaborated to investigate released fractions of representative radionuclides, Cs and CsI. In order to estimate sensitivity of inputs, which have a substantial influence on the core melt progression and the transportation process of radionuclides, a variance decomposition method is applied. Stochastic process, specifically a Dirichlet process, is applied to construct a surrogate model in sensitivity analysis as a substitute of the code. The surrogate model is cross-validated by comparing with corresponding results of MELCOR. The analysis with the simpler model avoids laborious computational cost so that importance measures for input factors are obtained successfully.
本間 俊充
Proceedings of 4th International MACCS Users Group Meeting, p.57 - 66, 2002/10
原子力施設の確率論的安全評価(PSA)の目的のために原研で開発された事故影響評価コードOSCAARは、CEC/NEA共催の国際比較計算で計算コードとしての機能を検証した後、おもに個々の計算モデル及び全体システムの妥当性検証に研究の重点を移した。レベル3PSAの計算結果に付随する不確実さの巾を評価し、不確実さに寄与する因子を明らかにするために、OSCAARの不確実さ・感度解析を実施している。事故影響評価にかかわる2種の不確実さのうち、統計的な不確実さの検討では、OSCAARで用いている大気拡散モデル(流跡線パフモデル)に適合した気象サンプリング手法を開発し、少ないサンプリング数で事故影響のスペクトルを効率よく推定することを実現した。また、主観的不確実さに関しては、パラメータの不確実さ伝播解析手法をOSCAARに結合し、個人の早期健康影響リスクを対象とした不確実さ・感度の予備解析を実施した。個々のモデルの妥当性検証では、IAEA主催BIOMASS計画の線量再構成シナリオにOSCAARの核種移行モデルを適用し、その性能を評価した。また、これら一連の研究成果をベースに、コードの適用として軽水炉モデルプラントのレベル3PSAを実施している。
武田 聖司; 木村 英雄
JAERI-Research 2002-014, 20 Pages, 2002/07
地層処分の安全評価に伴う不確かさのうち、パラメータ不確かさとモデル不確かさに起因した影響評価を目的として、確率論的評価手法(GSRW-PSA)の開発を行った。不確かさの影響評価に先立ち、人工バリア及び天然バリア中の核種移行評価モデルに関して決定論的なベンチマーク計算を行い、評価コードの特性・適用性を明らかにした。次に、GSRW-PSAを用いて、HLW処分の重要核種であるCs-135及びSe-79を対象とした人工バリア及び天然バリアに関するパラメータ不確かさ解析を行った。さらに、天然バリアにおける地質媒体の概念化の違いとして、多孔質媒体と亀裂性媒体による近似モデルを想定し、概念化の違いによる影響の評価を実施した。
M.Elert*; A.Butler*; J.Chen*; C.Dovlete*; A.Konoplev*; A.Golubenkov*; M.Sheppard*; 外川 織彦; T.Zeevaert*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 42, p.255 - 270, 1999/00
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:23.84(Environmental Sciences)BIOMOVS計画におけるモデル複雑さに関するサブワーキンググループでは、複雑さの異なるモデルを核種の土壌への浸透という問題に適用した。この目的は、モデル予測の不確かさがモデルの複雑さによって如何に変わるかまたモデルの簡略化を如何に行うべきかを検討することである。牧草土壌の表面汚染に関するシナリオを定義し、 Cs、
Cs、 Sr及び
Sr及び Iという3核種を計算対象とした。様々なモデルに必要となるパラメータの詳細な記述を、それらの不確かさとともに与えた。7機関から13種類のモデルがこのシナリオに参加した。これらのモデルは、2ボックスモデルから数値解析モデルまで様々であった。本報告では、設定されたシナリオ、参加したモデル、比較結果と議論、及び導かれた結論を記述する。
Iという3核種を計算対象とした。様々なモデルに必要となるパラメータの詳細な記述を、それらの不確かさとともに与えた。7機関から13種類のモデルがこのシナリオに参加した。これらのモデルは、2ボックスモデルから数値解析モデルまで様々であった。本報告では、設定されたシナリオ、参加したモデル、比較結果と議論、及び導かれた結論を記述する。
村尾 良夫
混相流, 11(3), p.203 - 204, 1997/00
混相流工学の発展における問題点の指摘と、その解決のための日本混相流学会の役割について述べる。混相流のように、現象が複雑であり、微視的に定式化されていないが、実用的には、広く使われているもので、現象把握の不確実さをいかに克服して安全に使うかが重要である。現象の研究から実用までのプロセスを概観し、その過程に含まれる「人間の判断」はどのようなものかを指摘する。人間の判断の誤りを減らすためには、多数の専門家が関与するのが有効であることから、専門家集団としての学会の役割を論ずる。
外川 織彦
保健物理, 29, p.55 - 64, 1994/00
国際協力研究BIOMOVS計画が、スウェーデン国立放射線防護研究所などの主催によって1986年から実施されている。この計画は、放射性核種あるいは安定微量物質の生態圏における移行と蓄積を予測するためのモデルの妥当性を検証することを目的としている。原研は当初よりこの計画に参加してきた。本報告では、BIOMOVS計画の概要に関して、1990年まで行われたPhase Iにおける検証シナリオとここで得られた成果を原研が参加したシナリオを中心に報告し、さらに1992年に開始されたPhase IIにおける研究テーマと今後の展望を紹介する。
本間 俊充; 笹原 孝*
JAERI-M 93-207, 36 Pages, 1993/10
本報告書は、OECD/NEA主催のPSAC利用者グループの比較問題レベル0に、開発中の確率論的システム評価コードを適用した結果を示すものである。この比較問題は、廃棄物の地層処分施設の性能評価に用いる確率論的システム評価コードの比較検証を目的として提案されたものの一つである。計算には、入力パラメータ値のサンプリングのためのプリ・プロッセッサーコードPREPと不確かさ/感度解析のためのポスト・プロッセッサーコードUSAMOを用い、廃棄物処分システムを構成する各サブシステムモデルは、レベル0の問題設定にしたがってコード化したものを用いた。比較問題の設問への回答の他に、不確かさ及び感度解析を行い、その結果も記載した。
本間 俊充; A.Saltelli*
EUR-13922, 33 Pages, 1992/00
PREPコードはプログラム化されたモデルの挙動をモンテカルロ解析で行うための支援コードである。この種の解析の目的は、入力パラメータに対するモデル応答を決定し、モデル予測値の不確かさを評価し、その不確かさに最も関係する入力パラメータを見い出すことにある。PREPが扱う部分は、与えられた入力パラメータの分布関数に従って入力パラメータの値の組を準備することである。PREPは一組の入力パラメータの組に対して解析を実行するユーザプログラムを複数の組に対しても実行できるように変更させる。ここでは、モデルの概略と2つの適用例を与えてユーザーの指針をする。
外川 織彦
保健物理, 24, p.166 - 169, 1989/00
国際共同研究BIOMOVSは生態圏における放射性核種あるいは微量物質の移行・蓄積を予測するモデルの正確さを検証するために、スウェーデン国立放射線防護研究所の主催により1985年から行われている。この研究は実測データによるモデル予測の検証及びモデル予測とそれに付随する不確かさの相互比較という2つの検証方法で進められ、各々に対して数種の検証シナリオが提案された。これらのシナリオに対してモデル予測による比較・検討が進められている。第7回BIOMOVSワークショップ及び調整グループ会議が、昭和63年11月に日本原子力研究所東海研究所で開催された。この会議には11ケ国21機関、1国際機関より35名が参加した。本稿では、BIOMOVS計画の概要、日本での会議における主な議論、今後の予定について紹介する。
Zheng, X.; 杉山 智之
no journal, ,
A suite of methodologies has been developed at JAEA for the source term uncertainty and sensitivity analyses during nuclear reactor severe accidents. Using the methodologies and integral severe accident codes, the uncertainty range of source term estimation can be quantified, and most influential factors can be identified. As shown in the results, some parameters from core component failure models have significant importance on the source term analysis. This study can lay groundwork for the improvement of numerical core component failure modeling in integral nuclear reactor severe accident simulation.